A significant international survey has revealed that political considerations are increasingly shaping electric vehicle purchasing decisions worldwide, with Tesla emerging as the most avoided brand due to its political associations.
Global Resistance to Tesla
The comprehensive poll conducted for the Global EV Alliance during September and October surveyed more than 26,000 electric vehicle owners across 30 countries. The findings demonstrate that political factors now play a substantial role in consumer choices, with 53 percent of respondents admitting they would avoid specific brands or countries of production based on political considerations.
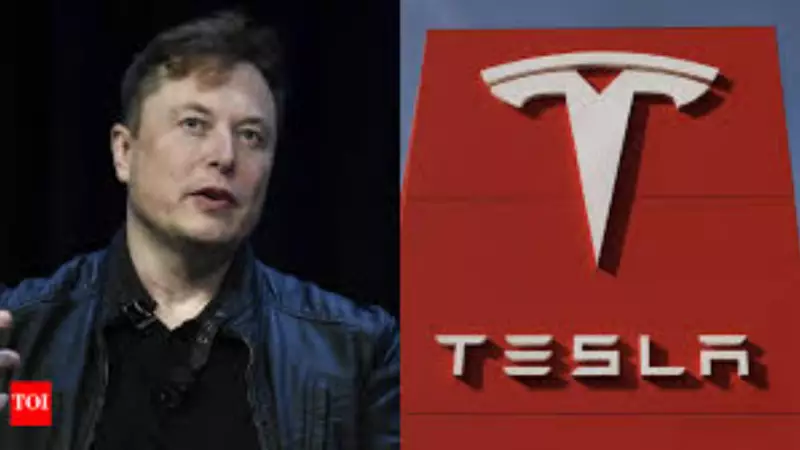
When participants identified which brands they would specifically avoid, 41 percent named Tesla as their primary concern. This placed the Elon Musk-led company significantly ahead of other avoided categories, with only 12 percent expressing reservations about China-made models and a mere 5 percent avoiding American-made vehicles in general.
Regional Variations in Tesla Perception
The survey uncovered substantial geographic differences in attitudes toward Tesla. Resistance was particularly strong in developed markets, with 52 percent of American EV drivers expressing reluctance to purchase Tesla vehicles. German consumers showed similar skepticism at 51 percent, while Australia and New Zealand recorded 45 percent avoidance rates.
Even in Norway, which leads global EV adoption with the highest penetration rate worldwide, 43 percent of respondents indicated they would steer clear of Tesla brands. This widespread resistance contrasts sharply with the Indian market, where only 2 percent of EV drivers reported any hesitation about purchasing Tesla vehicles.
Elon Musk's Political Controversies
The survey findings coincide with increasing political controversies surrounding Tesla CEO Elon Musk. The billionaire entrepreneur has drawn significant criticism for his close alignment with former US President Donald Trump during the cost-cutting "Department of Government Efficiency" initiative, though the two later clashed over federal budget priorities.
Musk has additionally faced backlash for supporting far-right groups in Europe, publicly opposing diversity policies, and making gestures that numerous observers interpreted as Nazi salutes. These actions have sparked boycott calls across multiple countries, though the actual impact on Tesla sales remains uncertain.
Varied Attitudes Toward Chinese EVs
The survey also highlighted diverse global perspectives on Chinese-manufactured electric vehicles. While 12 percent of global respondents stated they would avoid EVs made in China, national attitudes varied dramatically. Lithuanian drivers showed the strongest resistance at 43 percent, while Italian and Polish consumers demonstrated minimal concern with only 2 percent avoidance rates each.
Ellen Hiep, a steering committee member at Global EV Alliance, explained to AFP that economic realities influence preferences in developing markets. "In the Global South, people don't have too much choice. So I think sometimes they want to drive electric, and they want to have an affordable car while maybe in Europe and the US, we've got a bigger choice," Hiep noted, highlighting how purchasing decisions differ between developed and developing economies.
The survey results indicate that political branding is becoming increasingly important in the competitive electric vehicle market, potentially affecting manufacturer strategies and consumer choices as the global transition to electric mobility accelerates.