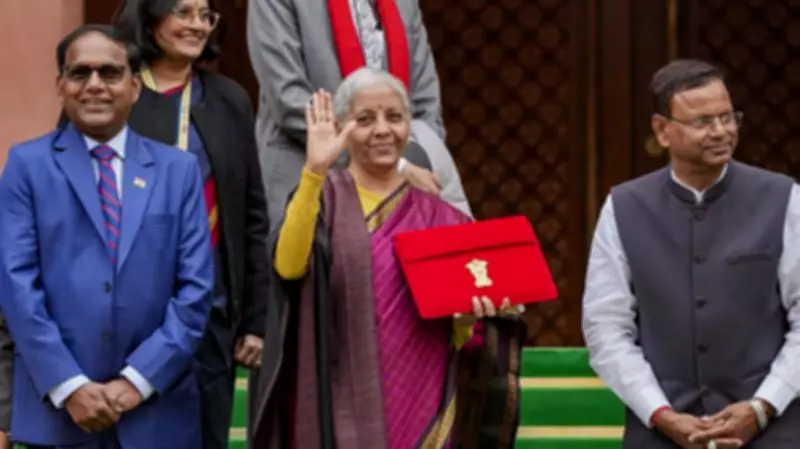
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget for the fiscal year 2026-27, outlining a comprehensive roadmap aimed at accelerating India's economic growth and infrastructure development. The budget introduces significant initiatives across transportation, manufacturing, healthcare, and financial sectors, with a strong emphasis on achieving the Viksit Bharat vision.
Infrastructure and Transportation Boost
The budget places a heavy focus on enhancing India's logistics and connectivity networks. A major highlight is the establishment of new dedicated freight corridors, specifically connecting Dankuni in the eastern region to Surat in the west. This project is expected to streamline cargo movement and reduce transportation costs significantly.
Additionally, the government plans to operationalize 20 new national waterways, strategically linking mineral-rich areas, industrial centers, and key ports. This move aims to boost inland water transport, which currently has a modest share in the country's freight movement.
Coastal and Industrial Development
To further promote maritime trade, a Coastal Cargo Promotion Scheme will be launched with an ambitious target: increasing the share of inland waterways and coastal shipping from 6 percent to 12 percent by 2047. The budget also includes the Purvodaya initiative, which focuses on developing an Integrated East Coast Industrial Corridor to spur economic activity in eastern states.
Economic and Tax Reforms
In a bid to attract foreign investment, the budget offers a tax holiday up to 2047 for foreign companies providing services globally from India. A safe harbour provision is introduced for non-residents involved in component warehousing within bonded warehouses, simplifying compliance.
The financial sector sees reforms with a comprehensive review of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) Non-debt Instruments Rules. A market-making framework and total return swaps on corporate bonds will be introduced to deepen the bond market.
Manufacturing and Sectoral Schemes
To boost domestic production, three dedicated chemical parks will be set up. The budget also includes a scheme for rare earth permanent magnets, covering research, mining, processing, and manufacturing. High-value construction equipment manufacturing will be strengthened to support infrastructure projects.
In textiles, the Tex-eco initiative aims to promote globally competitive and sustainable apparel. For real estate, Central public sector enterprises' assets will be recycled through dedicated Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), unlocking value.
Healthcare and Education Initiatives
The healthcare sector receives attention with schemes to support states in establishing five hubs for medical value tourism in partnership with the private sector. Upgrading and establishing new institutions for allied health professionals in 10 disciplines is planned to enhance workforce capacity.
In education, a high-powered 'education to employment and enterprise' standing committee will focus on the services sector. Three new All India Institutes of Ayurveda will be set up, with upgrades to AYUSH pharmacies and drug testing labs to promote traditional medicine.
Agriculture and Rural Development
Agricultural initiatives include rejuvenating old low-yielding orchards and expanding high-density cultivation of walnuts, almonds, and pine nuts. A coconut promotion scheme aims to increase production and productivity, while Indian Cashew and Cocoa Programmes receive support.
For veterinary services, loan-linked capital subsidy support will be provided for establishing hospitals and diagnostic laboratories. The fisheries value chain in coastal areas will be strengthened, and integrated development of 500 reservoirs and Amrit Sarovars is planned for water resource management.
Urban and Financial Measures
Urban development continues with the current AMRUT scheme, and an incentive of Rs 100 crore is offered for single issuances of municipal bonds exceeding Rs 1,000 crore to fund local projects. The Power Finance Corporation (PFC) and Rural Electrification Corporation (REC) will be restructured to improve efficiency in the power sector.
A high-level committee on banking for Viksit Bharat will be set up to align financial services with India's next growth phase, ensuring that the banking sector supports broader economic goals.