Microsoft is revolutionizing personal computing with a groundbreaking AI feature for Windows 11 that could fundamentally change how users interact with their computers. The tech giant has unveiled Agent Workspace, an experimental capability that positions Windows 11 as an AI-first operating system where artificial intelligence agents work autonomously in the background while users continue their normal activities.
What is Agent Workspace and How It Functions
Agent Workspace represents Microsoft's ambitious vision for the future of computing. This innovative feature creates separate, contained Windows sessions exclusively dedicated to AI agents. Each AI agent operates within its own isolated environment complete with a dedicated desktop, user account, permission set, and runtime system.
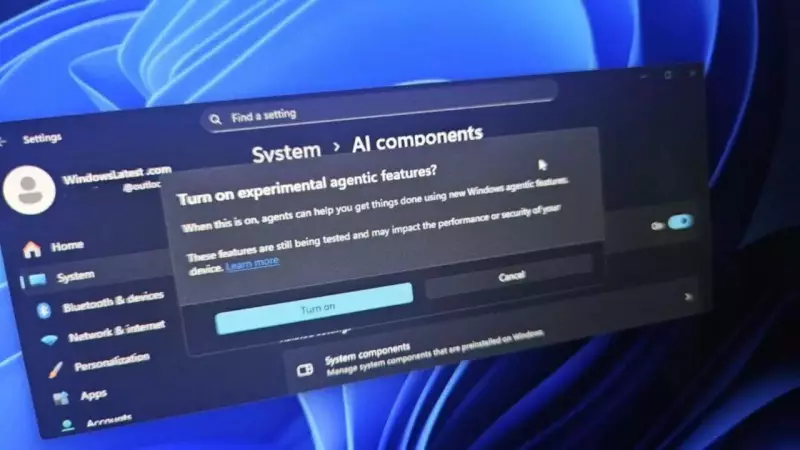
This isolation ensures that AI activities don't interfere with or disrupt the user's primary desktop experience. The feature is currently available only to Windows Insiders, Microsoft's testing community that helps refine new capabilities before public release. Users can activate this optional feature through Settings by navigating to System, then AI Components, and finally selecting Experimental Agentic Features.
Once enabled, AI agents can perform various tasks simultaneously with the user's regular workflow. These automated assistants can open applications, manage files efficiently, execute scripts, and handle numerous other functions that typically require manual intervention.
AI Access to Personal Files and Security Measures
The capability of AI agents to access and manage personal files marks a significant shift in how operating systems function. Agent Workspace provides AI with access to Windows' Known Folders including Documents, Desktop, Downloads, Pictures, Music, and Videos. This comprehensive access enables AI agents to locate and manage files even when users have relocated these folders within their system.
With read and write permissions to these crucial directories, AI agents can automate repetitive tasks such as organizing documents systematically, creating presentations automatically, updating media libraries, and performing various file management operations. Microsoft has implemented scoped authorization, meaning each agent operates with individually defined permissions, preventing any single agent from having blanket access across the system.
Microsoft emphasizes that all agent actions remain auditable and controllable, providing users with complete visibility into what AI agents are doing within their systems. This transparency is crucial for maintaining user trust and ensuring security compliance.
Security Architecture and Future Implications
While Agent Workspace might initially resemble Windows Sandbox, Microsoft highlights critical differences in their security approach and functionality. The system enables parallel execution where agents operate alongside the main desktop without causing interruptions. Each agent maintains separate accounts and permission sets, creating natural barriers between different AI functions.
Unlike Windows Sandbox, which establishes a completely isolated virtual environment that erases all activities upon closure, AI agents within Agent Workspace can access personal folders while running. This distinction is essential for the practical utility of AI assistants while maintaining security protocols.
Microsoft continues to refine the security model with a clear focus on transparency, safety, and user control. The company aims to strike a delicate balance between innovative AI capabilities and robust security measures. As Windows 11 evolves toward becoming an AI-native operating system, features like Agent Workspace demonstrate Microsoft's commitment to local AI assistance that automates repetitive tasks and enhances productivity.
However, granting AI agents access to personal files inevitably raises legitimate privacy and security concerns that Microsoft must address comprehensively. The experimental nature of this feature and its limited availability to Windows Insiders provides an opportunity for thorough testing and refinement based on real user feedback before any potential wider release.
This development represents Microsoft's strategic push to integrate AI more deeply into everyday computing experiences, potentially transforming how millions of users interact with their Windows devices for work and personal use.





