UPSC Essentials: Mains Answer Practice for GS 3 – Week 139
Are you gearing up for the Civil Services Exam 2026? This week's UPSC Essentials initiative focuses on enhancing your Mains answer writing skills through targeted practice on crucial topics from GS Paper 3. Designed as a valuable addition to your preparation, this session helps you refine your responses and deepen your understanding of static and dynamic syllabus components.
Key Questions for This Week's Practice
This edition presents two pivotal questions that align with current affairs and core UPSC themes. Engaging with these topics will bolster your ability to articulate well-rounded answers in the Mains examination.
Question 1: Hypersonic Missile Technology
India's successful development of hypersonic glide missile technology marks a significant leap in its strategic deterrence and defence preparedness. Discuss the strategic and technological implications of this development.
Relevance: This topic is highly pertinent for GS 3 under Defence Technology, Internal Security, and Science & Technology. It encompasses strategic deterrence, military modernisation, indigenisation of defence technology, and emerging warfare systems, all of which are central to UPSC Mains.
Introduction:
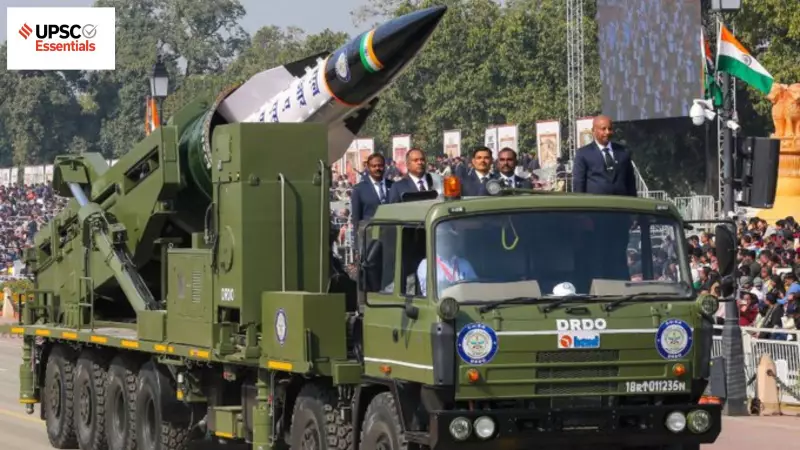
- At the 77th Republic Day Parade on Kartavya Path, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) showcased the Long Range Anti-Ship Hypersonic Missile (LR-AShM) for the first time.
- This missile system is tailored to meet the coastal battery requirements of the Indian Navy, capable of engaging both static and moving targets with a range of approximately 1,500 kilometers.
Body Points to Incorporate:
- The LR-AShM follows a quasi-ballistic trajectory, achieving hypersonic speeds starting at Mach 10 and maintaining an average of Mach 5 with multiple skips. This design allows it to evade interception by flying at low altitudes with high manoeuvrability.
- Its propulsion system features a two-stage solid rocket motor, boosting it to hypersonic velocities. After burnout, the vehicle glides unpowered, performing necessary manoeuvres before target engagement.
- High aerodynamic efficiency enables the missile to move through air with minimal drag, enhancing its range, speed, and accuracy using the same energy input.
- Hypersonic speeds make detection challenging for enemy radars, allowing the missile to cover 1,500 kilometers in about 15 minutes. Versions with ranges up to 3,500 kilometers are under development.
Conclusion:
- The LR-AShM can neutralise all classes of warships, serving as a key asset for sea denial operations that prevent adversaries from using maritime areas.
- DRDO is advancing two hypersonic technologies: glide and cruise. The LR-AShM, as a hypersonic glide vehicle, showcases indigenous achievements in materials and control systems for sustained hypersonic flight.
Points to Ponder: Explore more about hypersonic missiles and ramjet engines. Consider related previous year questions on topics like India's fusion energy programme and semiconductor manufacturing challenges.
Question 2: Goldilocks Economy
India is currently witnessing a 'Goldilocks phase' characterised by high growth and low inflation. What is a 'Goldilocks economy'? Discuss the macroeconomic factors behind this phase and the structural challenges that may threaten its sustainability.
Relevance: This topic directly falls under Indian Economy in GS 3, covering growth, inflation, macroeconomic stability, fiscal and monetary policy, and structural reforms, all high-priority areas for Mains.
Introduction:
- Recently, the RBI Governor described India's macroeconomic moment as a "rare goldilocks period," marked by high economic growth and exceptionally low inflation.
- According to NSO's first advanced estimates, real GDP growth is projected at 7.4% in FY26, with nominal growth at 8% and CPI inflation around 2%, despite global trade tensions and geopolitical risks.
Body Points to Incorporate:
- Domestic tailwinds, such as sustained increases in capital expenditure by both the Centre and states, are expected to prolong the Goldilocks period into FY26-27 and beyond.
- Reforms in income tax and GST, along with unconditional cash transfers to women and reduced interest rates, are likely to boost consumption and growth.
- A diverse export portfolio and well-designed free trade agreements can mitigate reliance on specific industries or destinations, supporting economic stability.
- The current account deficit remains under control, providing grounds for confidence, though policymakers must stay vigilant against global and domestic threats.
- To achieve developed nation status by 2047, India needs 7-8% growth, requiring a 4-5% increase in investment rates and higher savings rates.
Conclusion:
- Implementing reforms like labour codes and quality control orders, coupled with investments from major tech firms and initiatives in research and development, can drive private investment.
- Factors such as artificial intelligence efficiency gains, a young population, urban infrastructure development, women's empowerment, and structural shifts from agriculture to manufacturing and services will further bolster growth.
Points to Ponder: Reflect on the structural strengths that support sustainability and key policy priorities to maintain the Goldilocks phase. Review related previous year questions on fiscal health indices and labour codes.
Enhance Your Preparation
This answer-writing practice is not a model answer but a thought process to guide your responses. Incorporate these points to craft comprehensive answers and check your progress. For more resources, refer to previous weeks' practices and stay updated with UPSC-related news through newsletters and social media channels.