For aspirants of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) Civil Services Examination, staying abreast of current affairs and their intricate connections to the syllabus is paramount. The Indian Express UPSC Key for January 5, 2026, curated by Roshni Yadav, dissects several pivotal topics with significant relevance for both the Preliminary and Main stages of the exam. This analysis delves into the historical and cultural significance of the Somnath Temple, India's newfound status as the world's leading rice producer, the evolving dynamics of American foreign policy, and the critical implications of the European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
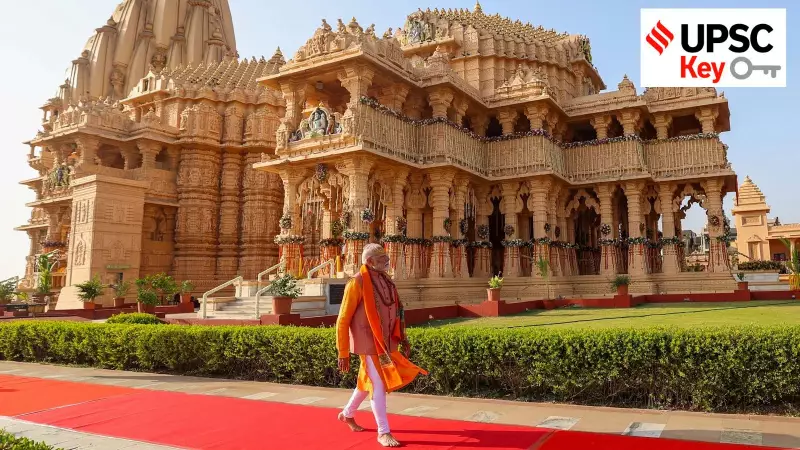
Somnath Swabhiman Parv: A Millennium of Unbroken Faith (1026-2026)
The year 2026 marks a profound milestone in India's cultural and historical narrative. It commemorates 1,000 years since the first invasion of the Somnath Temple by Mahmud of Ghazni in 1026. This event is not merely a historical footnote but a powerful symbol of civilizational resilience and cultural continuity, making it a crucial area of study for the UPSC.
Situated at Prabhas Patan on Gujarat's western coast, the Somnath Temple is revered as the first among the twelve Jyotirlingas, a fact highlighted in the Dwadasha Jyotirling Stotram. Its repeated destruction and reconstruction over centuries embody the enduring spirit of Indian faith and architecture.
Key Takeaways for UPSC Aspirants
Several critical points emerge from the Somnath narrative that are essential for exam preparation:
The 2026 significance is twofold: It marks a millennium since Mahmud of Ghazni's attack and also completes 75 years since the temple's restoration and re-consecration in 1951. The restored temple was inaugurated by Dr. Rajendra Prasad, India's first President, following a reconstruction initiative led by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
The temple's history offers a lens to examine early Indian temple architecture, broadly classified into the Nagara (northern) and Dravida (southern) traditions, with a potential third hybrid style called Vesara. Understanding this architectural evolution is key for the Art and Culture segment of General Studies Paper-I.
The event connects to broader themes of religion and politics in early India, the impact of foreign invasions on Indian society, and the post-independence efforts towards cultural revival, as inspired by figures like Swami Vivekananda.
America's Return to Interventionism: The Venezuela Case
In a dramatic shift in foreign policy, the United States, under President Donald Trump, has captured Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro. This action signals a stark return to the interventionist Monroe Doctrine, rebranded by Trump as the "Don-roe Doctrine." This development holds substantial relevance for UPSC's International Relations syllabus.
The primary driver behind this intervention appears to be Venezuela's vast oil reserves. The country possesses the world's largest proven crude oil reserves, estimated at over 300 billion barrels, yet its current production is a minuscule fraction of global output due to sanctions and infrastructural decay. The US aims to control and revitalize this sector.
Implications for India and Global Order
India's response to the crisis has been a careful diplomatic balancing act. The Ministry of External Affairs expressed "deep concern" and called for peaceful dialogue, without directly condemning the US. This reflects India's complex diplomatic position, navigating its strategic ties with Washington while addressing concerns from the Global South about unilateral actions.
For India's energy security, a stabilized and sanctions-free Venezuelan oil industry could be beneficial in the long term, though current imports are negligible. The event underscores the principle of non-intervention in international relations and the potential for resource-driven conflicts, key topics for GS Paper-II.
India Surpasses China as World's Largest Rice Producer
In a significant achievement for the agricultural sector, Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan announced that India's rice production reached 150.18 million tonnes in 2024-25, surpassing China's output of 145.28 million tonnes. This milestone is crucial for topics related to Indian Economy, Geography, and Government Policies.
On this occasion, the government released 184 new high-yielding seed varieties for 25 crops, including cereals, cotton, oilseeds, and pulses. Notably, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has developed the world's first genome-edited (GE) rice varieties, named 'Kamala' and 'Pusa DST Rice 1', which offer superior yields and stress tolerance.
Relevance for UPSC Preparation
Aspirants should focus on the factors behind this increased production, such as the adoption of high-yielding and climate-resilient seed varieties. They must also be aware of the associated challenges, including the environmental impact of rice cultivation as a major source of methane emissions, and the debate around practices like the System of Rice Intensification (SRI), which can reduce water and seed requirements.
This news ties directly to syllabus areas like Major Crops-cropping patterns, Government interventions in agriculture, and the application of biotechnology for societal upliftment.
The Swachh Survekshan and Urban Governance Challenges
The recent water contamination tragedy in Indore, which led to several deaths, has cast a shadow over the city's remarkable record of being ranked India's cleanest city for seven consecutive years in the Swachh Survekshan. The incident highlights the gap between rankings and ground-level governance in urban sanitation.
Indore's success in the surveys was built on parameters like 100% door-to-door waste collection, segregation at source, and remediation of dumpsites. It had even achieved the "Water+" certification, indicating no discharge of untreated wastewater. The tragedy underscores the critical importance of maintaining water supply infrastructure and the persistent threat of waterborne diseases.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM): A Green Challenge and Opportunity
The European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) has moved from a transitional to a definitive phase, imposing real carbon costs on imports like steel, aluminium, and cement. This policy, aimed at preventing "carbon leakage," has already impacted Indian exports, with steel shipments to the EU falling by over 51% as of FY26 projections.
India's Strategic Response
This climate-trade measure presents both a challenge and an opportunity. To comply and remain competitive, India must accelerate its National Green Hydrogen Mission, which targets 5 million metric tonnes per annum of green hydrogen production by 2030. Green hydrogen is vital for producing cleaner steel via Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) technology.
Experts argue that instead of contesting CBAM at the WTO for years, India should proactively build a robust carbon pricing architecture and leverage its renewable energy potential to become a global leader in green manufacturing. This aligns with India's ambitions for energy independence and net-zero emissions by 2070.
The UPSC Key for January 5, 2026, thus weaves together threads from history, international relations, agriculture, public policy, and environmental economics. For the discerning aspirant, these are not isolated news items but interconnected themes that test analytical depth and a multidimensional understanding of India and the world.