Premium UPSC Key: Essential Topics for January 24, 2026
For UPSC aspirants, staying updated with current affairs is paramount. The Indian Express UPSC Key for January 24, 2026, delves into critical issues spanning governance, international relations, health, demographics, and economics. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of key topics, their relevance to the UPSC Civil Services Examination, and actionable insights for both Preliminary and Main stages.
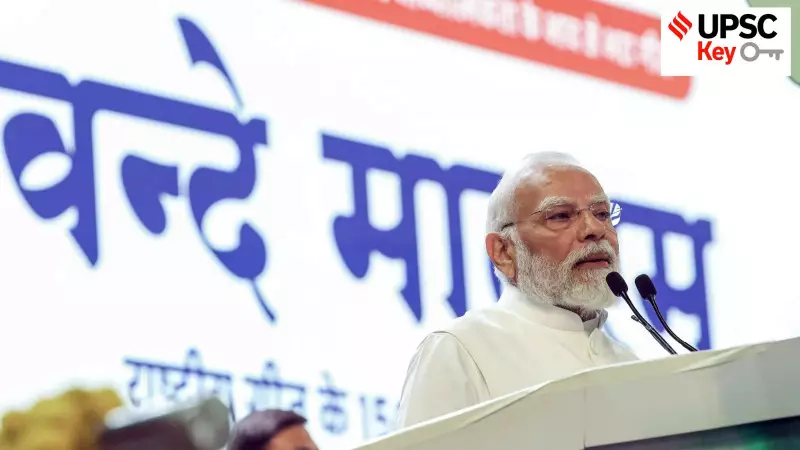
Government Debates Protocols for Vande Mataram
Syllabus Coverage: Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance. Mains Examination: General Studies-II: Government policies and interventions.
What’s the ongoing story: A high-level government meeting recently examined potential protocols for the national song Vande Mataram, akin to those for the national anthem Jana Gana Mana. This move aims to elevate the song's status, addressing historical and legal gaps.
Key Points to Ponder:
- History of Vande Mataram's adoption during the Swadeshi movement.
- Recent controversies and petitions seeking legal clarity.
- Comparison with the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971.
- Fundamental duties under Article 51A(a) of the Constitution.
Key Takeaways:
- Vande Mataram, written by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay, lacks compulsory etiquette or legal mandates, unlike the national anthem.
- The BJP-led government views this as an effort to counter perceived diminishment by previous administrations.
- Supreme Court rulings, such as Bijoe Emmanuel vs State of Kerala (1986), protect religious freedoms, while Shyam Narayan Chouksey vs Union of India (2018) made anthem playing in cinemas optional.
- This topic underscores the balance between national symbols and individual rights, crucial for Mains essays.
EU Leaders' Republic Day Visit: Strategic Implications
Syllabus Coverage: Preliminary Examination: Current events. Mains Examination: General Studies-II, III: Bilateral agreements, economic liberalization.
What’s the ongoing story: EU leaders' visit aims to conclude India-EU trade negotiations, enhancing supply chain diversification and reducing dependencies on China.
Key Points to Ponder:
- Significance of the India-EU trade deal for economic growth.
- Role in diversifying supply chains, especially in pharmaceuticals and high-tech sectors.
- Connection to the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
- Geopolitical context amid global fragmentation.
Key Takeaways:
- The visit by European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and European Council President Antonio Luís Santos da Costa highlights strategic partnerships.
- Trade agreement expected to boost investment in hydrogen, machinery, and advanced manufacturing.
- New mobility frameworks for students and professionals align with EU labor needs.
- Editorial insights emphasize India's strategic autonomy and Europe's cohesion post-Ukraine war.
Anti-Microbial Resistance: A Silent Health Crisis
Syllabus Coverage: Preliminary Examination: Current events. Mains Examination: General Studies-II: Health sector management.
What’s the ongoing story: Prime Minister Narendra Modi and other leaders have raised awareness about AMR, driven by antibiotic overuse, with India facing significant public health challenges.
Key Points to Ponder:
- Definition and status of AMR in India, including high resistance rates.
- Antibiotic stewardship versus over-the-counter sales bans.
- Government initiatives and behavioral changes needed.
- Alternative therapies like phage therapy.
Key Takeaways:
- An estimated 267,000 deaths in 2021 were attributable to AMR, with common infections becoming untreatable.
- Kerala's decade-long stewardship program shows gradual success, suggesting phased approaches are effective.
- Misuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics and viral infection treatments exacerbates resistance.
- WHO guidelines on antibiotic pollution highlight regulatory gaps, relevant for policy questions.
16th Census of India: Digital Innovations and Expanded Scope
Syllabus Coverage: Preliminary Examination: Indian Polity and Governance. Mains Examination: General Studies-II: Government policies.
What’s the ongoing story: The 16th Census, delayed by six years, will feature a digital-first houselisting phase from April to September 2026, introducing new questions and technologies.
Key Points to Ponder:
- Historical context of censuses in India since 1872.
- Differences between Census, caste census, and Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC).
- Role of the Registrar General of India (RGI).
- Impact on schemes like PM Awas Yojana and Jal Jeevan Mission.
Key Takeaways:
- Houselisting will map structures and households, using mobile apps, GPS tagging, and self-enumeration options.
- New questions cover internet access, smartphone ownership, vehicle types, and cereal consumption, reflecting societal shifts.
- Data will inform policymaking, with real-time monitoring via the Census Management and Monitoring System (CMMS).
- This topic is vital for understanding demographic trends and governance mechanisms.
RBI Urges States to Reduce Debt: Fiscal Challenges
Syllabus Coverage: Preliminary Examination: Current events. Mains Examination: General Studies-III: Indian economy, government budgeting.
What’s the ongoing story: The Reserve Bank of India has called for states to establish clear debt reduction paths, mirroring central government efforts, as high debt hampers investment and growth.
Key Points to Ponder:
- Concepts of debt-GSDP ratio and fiscal deficit.
- Reasons for elevated state debt, including pandemic impacts.
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act provisions.
- Global ratings agencies' concerns about general government debt.
Key Takeaways:
- State debt is projected to rise to 29.2% of GDP by March 2026, with several states exceeding 30% thresholds.
- Central government targets reducing debt-to-GDP ratio to 50% by 2030-31, emphasizing coordinated fiscal discipline.
- Increased borrowings and welfare schemes like free electricity strain state finances, affecting capital expenditure.
- This issue highlights intergovernmental fiscal relations and economic sustainability.
Additional Insights: Disturbed Areas Law and Editorials
Disturbed Areas Law: Rajasthan proposes a bill similar to Gujarat's 1991 Act, regulating property transfers in communally sensitive zones. Key debates involve constitutional rights under Articles 19(1)(e) and 15, and judicial oversight under Article 226.
Editorial Highlights: Pieces on Manipur's peace process, India's stance in the Trump era, and corporate sales data questioning GDP growth offer broader perspectives on governance and economics.
For UPSC aspirants, these topics are not only current but deeply interlinked with syllabus themes. Regular review of such analyses enhances answer-writing skills and factual retention, crucial for success in the examination.