US Reduces Tariffs on India to 18% in Landmark Trade Agreement
In a significant development for bilateral relations, the United States has agreed to lower tariffs on Indian goods to 18%, down from the previous rate of 50%. This major concession was announced as part of a comprehensive trade deal between the two nations, which came into effect on August 27. The new tariff structure provides India with a slight advantage over other South East Asian countries, including Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Pakistan, which continue to face American tariffs of 19%.
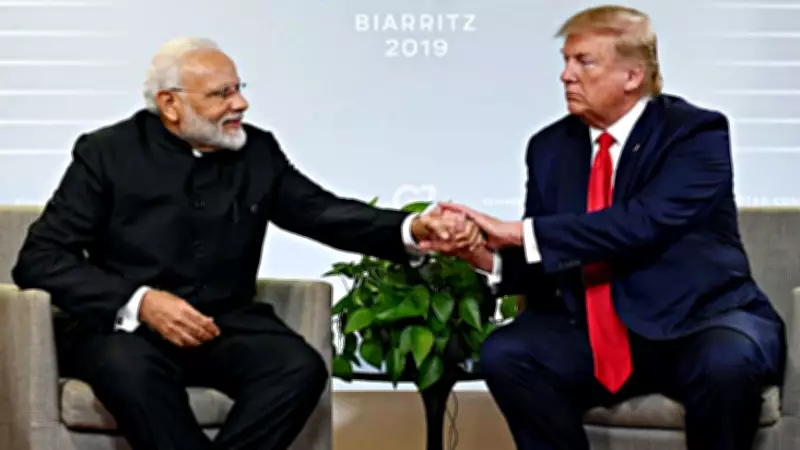
Trump and Modi Announce Deal with Reciprocal Benefits
US President Donald Trump and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi confirmed the agreement in separate statements. Trump emphasized the friendship and respect between the two leaders, noting that the reduced reciprocal tariff would immediately benefit trade relations. In response, Prime Minister Modi expressed his delight, highlighting that Made in India products would now enjoy more favorable access to the US market.
This tariff reduction positions India more competitively compared to key regional rivals, while the European Union, the United Kingdom, Japan, and South Korea maintain rates between 10% and 15%.
India's Commitments Under the Trade Deal
As part of the agreement, India has made substantial commitments to enhance economic cooperation with the United States. These include:
- Ceasing purchases of Russian oil and increasing imports from the US and potentially Venezuela.
- Purchasing $500 billion worth of US energy, agriculture, coal, and other products over the duration of the deal.
These steps align with recent Indian policy measures, such as the Union Budget proposals that offer tax incentives for foreign companies, particularly in cloud services and data centers. The budget includes a tax holiday until 2047 for global companies using Indian data center services, a move that directly benefits American tech giants.
Broader Economic Implications and Sectoral Benefits
The trade deal and accompanying budget measures signal a deeper economic integration between India and the US. Key sectors set to benefit include:
- Aviation: Elimination of duties on aircraft components and Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) inputs, supporting US aerospace firms.
- Nuclear Energy: Zero customs duty on nuclear-generation equipment until 2035, following the SHANTI Act of 2025, which opens the sector to private players.
- Textiles: Capital support for machinery and schemes to boost input availability, addressing long-standing challenges in the domestic industry.
Additionally, the US has secured greater market access for its companies looking to establish data centers in India, with demands for tax breaks and resource access being addressed through the budget's incentives.
Future Outlook and Investment Trends
American companies are already responding to these opportunities, with significant investments announced in India's data center infrastructure to support artificial intelligence growth. Union IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw projected that private investments in AI infrastructure could double from $70 billion in the previous financial year.
This trade deal not only strengthens economic ties but also reflects strategic alignment between India and the US, paving the way for enhanced cooperation in technology, energy, and manufacturing. The reduced tariffs and reciprocal commitments mark a new chapter in bilateral trade, with potential long-term benefits for both economies.