India-US Trade Agreement: A Breakthrough with Lingering Questions
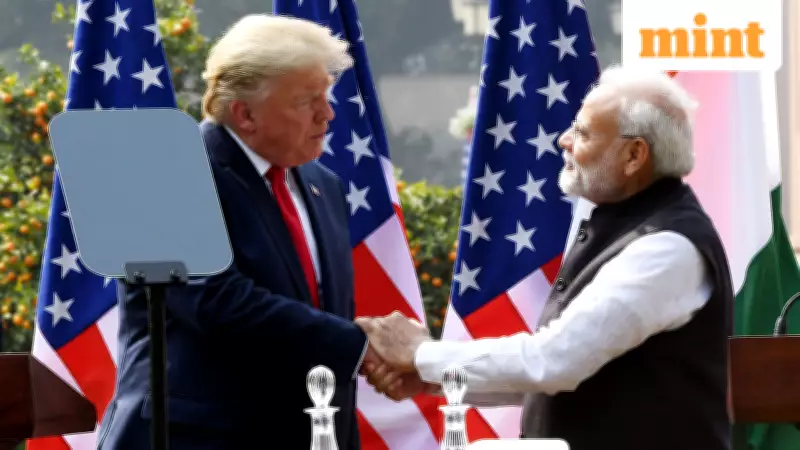
The recent trade agreement between India and the United States marks a significant diplomatic achievement, yet critical details regarding agricultural products remain unresolved. After enduring punitive tariffs for over five months, India has secured a reduction from 50% to 18%, providing relief to its manufacturing sectors and positioning the country favorably against competitors like Vietnam.
Key Components of the Agreement
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and US President Donald Trump have announced a preliminary deal that addresses several trade barriers. The agreement includes:
- Tariff reductions on Indian exports to the US, lowering duties from 50% to 18%.
- Energy cooperation with potential purchases of US hydrocarbons, including shale gas byproducts and Venezuelan crude.
- Market access discussions covering technology, agriculture, and coal products.
However, the fine print on agricultural items—historically a contentious issue—has yet to be fully disclosed, leaving stakeholders uncertain about the deal's comprehensive impact.
Agricultural Concerns and Unanswered Questions
Agricultural trade remains a sticking point in the India-US relationship. Key unresolved issues include:
- Genetically modified crops: Will India relax its ban on GM food imports despite domestic restrictions?
- Ethanol blending: US corn could supply India's ethanol needs, but political and farmer resistance may hinder adoption.
- Export restrictions: India's wheat export ban, imposed after the Ukraine conflict, raises questions about farm trade liberalization.
Opposition parties are expected to closely scrutinize any concessions on agriculture, given its sensitivity in Indian politics and the need to protect local farmers.
Broader Implications for India's Economy
The trade deal arrives at a crucial time for India's economic strategy. The threat of losing access to the US market has prompted New Delhi to diversify its trade partnerships, securing agreements with the UK and EU. These accords aim to reduce non-tariff barriers and improve quality standards, aligning India more closely with global trade norms.
Additionally, the deal could ease tensions in the technology sector, where US restrictions on work visas have impacted Indian professionals. Any concessions on H-1B visa fees or tech trade would be welcomed by India's urban middle class and IT industry.
Energy Security and Global Markets
Energy forms a critical component of the agreement. Trump's announcement suggests India may reduce its reliance on Russian oil in favor of US and Venezuelan supplies. However, Modi's statement omitted specific references to Russian energy, leaving room for interpretation.
The deal's energy provisions could reshape global hydrocarbon markets, particularly if Indian refiners shift their sourcing strategies. Questions remain about whether India will retain flexibility to trade with Iran or other suppliers amid US sanctions.
Conclusion: A Work in Progress
While the India-US trade deal represents a positive step toward resolving long-standing disputes, its success hinges on the clarification of agricultural terms and energy commitments. As both nations move to finalize the agreement, stakeholders await detailed provisions that will determine its true impact on trade, security, and bilateral relations.
The agreement underscores India's evolving approach to global trade, balancing economic interests with diplomatic priorities. As negotiations continue, the focus will remain on ensuring that the deal benefits all sectors, including agriculture, which remains vital to India's economy and political landscape.