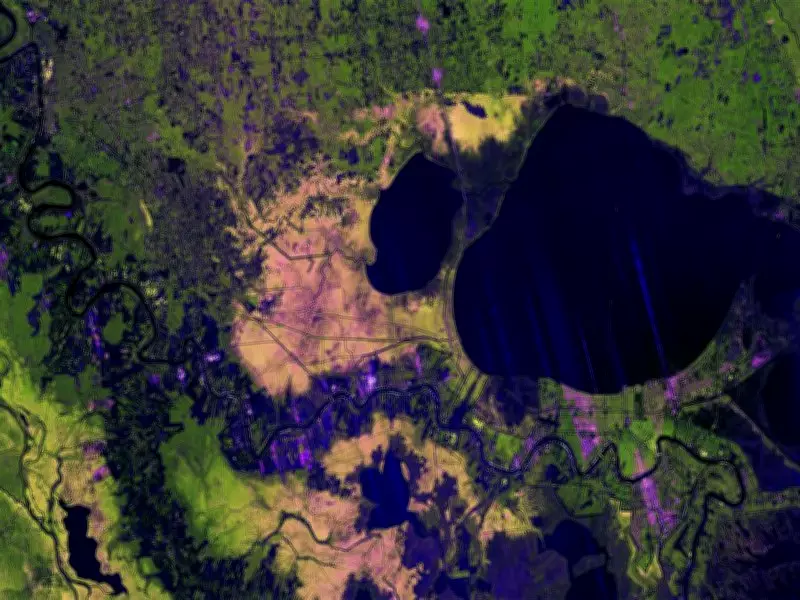
NASA-ISRO Radar Mission Achieves Breakthrough in Mapping Mississippi Delta
In a significant demonstration of international space collaboration, the joint NASA-ISRO NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) mission has successfully mapped the Mississippi River Delta with remarkable precision. This achievement showcases the mission's advanced radar capabilities, which can penetrate cloud cover and darkness to deliver detailed Earth observations.
Unprecedented Detail Through Advanced Technology
The NISAR mission utilized its sophisticated L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar to create high-resolution maps of the Mississippi Delta region. This technology allows scientists to observe subtle changes in land surfaces, water bodies, and vegetation with an accuracy previously unattainable. The radar's ability to operate regardless of weather conditions or time of day represents a major leap forward in Earth monitoring.
This mapping effort provides invaluable data for understanding delta dynamics, coastal erosion, and environmental changes in one of North America's most critical ecosystems. Researchers can now track minute alterations in the landscape that might indicate shifts in sediment flow, wetland health, or potential flood risks.
Implications for Global Environmental Monitoring
The successful mapping of the Mississippi Delta serves as a powerful proof of concept for the NISAR mission's broader objectives. Once fully operational, this satellite will systematically observe Earth's land and ice-covered surfaces every 12 days, creating a comprehensive dataset for climate and environmental studies.
- Enhanced monitoring of natural disasters such as floods, landslides, and earthquakes
- Improved understanding of carbon storage in forests and wetlands
- Better tracking of agricultural productivity and water resource management
- More accurate assessment of infrastructure stability and urban development impacts
The collaboration between NASA and ISRO exemplifies how international partnerships can advance scientific knowledge and address global environmental challenges. By combining American and Indian technological expertise, the NISAR mission promises to revolutionize our ability to observe and understand planetary changes.
Future Applications and Scientific Value
Beyond the Mississippi Delta demonstration, the NISAR mission's capabilities will support numerous scientific and practical applications. The radar's sensitivity to millimeter-scale surface movements will help monitor tectonic activity, glacier flow, and groundwater depletion with unprecedented detail.
- Climate change research through precise measurement of ice sheet dynamics
- Disaster management by providing near-real-time data on natural hazards
- Agricultural planning through detailed soil moisture and crop health monitoring
- Infrastructure assessment by detecting subtle ground movements that might indicate structural risks
This successful mapping exercise confirms that the NISAR mission is on track to become one of the most valuable Earth observation tools ever deployed, offering scientists and policymakers reliable data to make informed decisions about environmental management and disaster preparedness.