Central Government Directs Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to Divert Water for Yamuna Revival
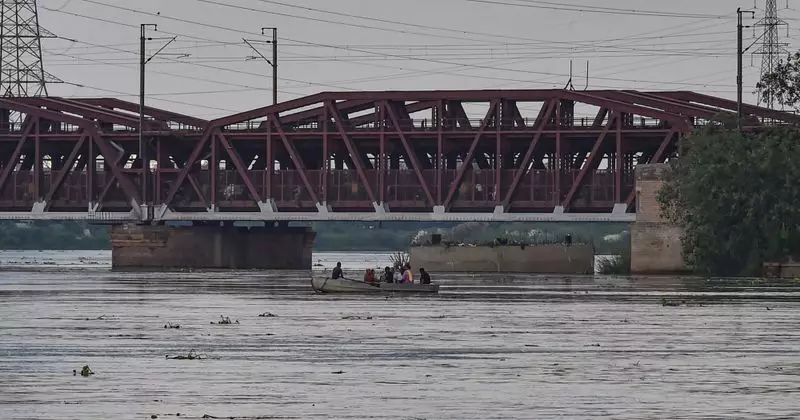
In a significant move to address the severe pollution and ecological degradation of the Yamuna River, the Central Government has issued formal directives to the states of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh. The orders mandate the diversion of water from the Munak Canal and the Ganga River to help revive the critically polluted stretches of the Yamuna, particularly in the National Capital Region of Delhi.
Key Directives for Water Diversion
The directive specifically requires Haryana to release additional water from the Munak Canal into the Yamuna. This canal, which originates from the Munak headworks in Haryana, is a crucial source of water for Delhi and plays a vital role in the region's water supply infrastructure. Simultaneously, Uttar Pradesh has been instructed to divert water from the Ganga River to supplement the flow in the Yamuna, aiming to improve its water quality and ecological health.
Background and Urgency of the Yamuna Crisis
The Yamuna River, one of India's major rivers, has been facing extreme pollution levels for decades, especially in the Delhi segment. Factors such as industrial discharge, untreated sewage, and reduced natural flow have turned the river into a highly contaminated water body, posing serious environmental and public health risks. The current initiative is part of broader efforts by the government to rejuvenate the river and restore its ecological balance.
Expected Impact and Implementation
By diverting water from the Munak Canal and Ganga River, authorities hope to:
- Increase the flow in the Yamuna, which can help dilute pollutants and improve water quality.
- Support aquatic life by providing a healthier habitat in the river ecosystem.
- Address water scarcity issues in Delhi, as enhanced flow can also contribute to the city's water supply needs.
The implementation of these directives is expected to be coordinated between the central and state governments, with monitoring mechanisms in place to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
Challenges and Future Steps
While this move is a positive step, challenges such as inter-state water sharing disputes, infrastructure limitations, and the need for sustained efforts in pollution control remain. The government may also consider additional measures, including stricter enforcement of pollution norms and community awareness campaigns, to ensure long-term revival of the Yamuna River.