Premium UPSC Key Analysis: Crucial Topics for Civil Services Examination
For UPSC aspirants preparing for the 2026 examinations, several significant developments demand careful attention across multiple subjects. The recent India-European Union Free Trade Agreement, updated University Grants Commission regulations addressing campus discrimination, innovative self-enumeration methods for Census 2027, and shifting American positions on international climate agreements represent critical areas of study that span current affairs, international relations, social justice, governance, and environmental policy.
India-EU Free Trade Agreement: A Strategic Milestone
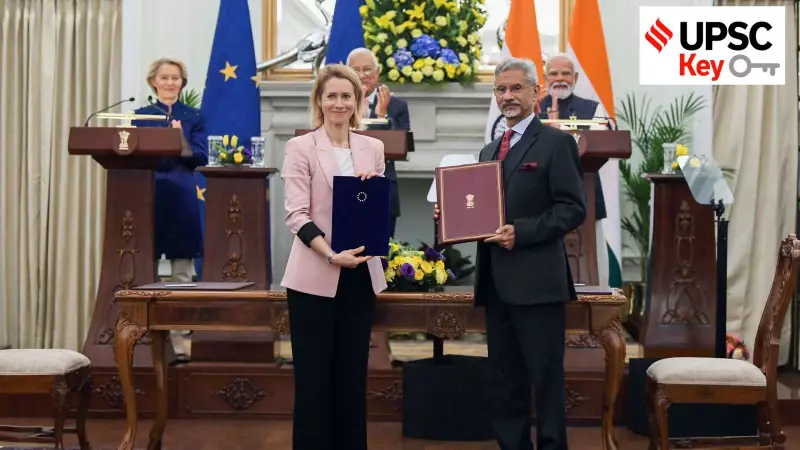
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar and EU High Representative Kaja Kallas exchanged documents at Hyderabad House in New Delhi, marking the conclusion of negotiations for what both sides termed "a new blueprint" and "the mother of all deals." This agreement represents a landmark achievement after nearly two decades of discussions between economic partners representing approximately two billion people.
The comprehensive FTA will eliminate duties on 99.5% of Indian exports, including textiles and gems, while reducing tariffs on 97% of EU goods such as automobiles and wines to zero in many cases. Beyond economic dimensions, the pact includes a security and defence partnership, mobility framework, and joint strategic agenda extending through 2030.
Several geopolitical factors accelerated these negotiations, including shifting American trade policies under the Trump administration and shared concerns about China's economic dominance. The agreement also advances the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, widely viewed as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative.
For UPSC preparation, candidates should examine:
- The evolution of India-EU relations since the strategic partnership declaration
- Key provisions of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
- Implications of the mobility pact for Indian students and professionals in EU countries
- Geopolitical considerations influencing contemporary trade agreements
UGC Equity Regulations: Addressing Campus Discrimination
The University Grants Commission has notified updated regulations titled "Promotion of Equity in Higher Education Institutions" to combat discrimination based on caste, gender, disability, and other protected categories. These regulations replace the 2012 framework with more robust institutional mechanisms and enforcement provisions.
Key features include mandatory establishment of Equal Opportunity Centres, Equity Committees with reserved category representation, mobile Equity Squads for campus vigilance, and 24-hour helplines for reporting incidents. Unlike the previous advisory approach, the 2026 regulations empower the UGC to impose sanctions on non-compliant institutions, including exclusion from funding and degree-granting authority.
The regulations specifically mention Other Backward Classes alongside Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in defining caste discrimination, reflecting broader inclusion. However, the framework has generated debate about potential misuse and the absence of penalties for false complaints.
UPSC aspirants should consider:
- Constitutional provisions regarding equality and social justice
- Historical context of caste-based discrimination in educational institutions
- Comparative analysis of the 2012 and 2026 regulatory frameworks
- Broader implications for social inclusion policies in higher education
Census 2027: Digital Transformation Through Self-Enumeration
The upcoming national census introduces innovative self-enumeration facilities allowing citizens to submit demographic information through a multilingual digital portal. Available in sixteen languages including Assamese, Bengali, Hindi, Tamil, and Urdu, this system represents a significant technological advancement in India's decadal population counting exercise.
Participants will receive a unique reference ID after completing the online schedule, which must be shared with local enumerators for verification. The self-enumeration window opens fifteen days before house-listing operations commence in each state or union territory.
Census 2027 will collect data on thirty-three parameters during the house-listing phase, with the Registrar General of India implementing a comprehensive Census Management and Monitoring System for real-time oversight. The government has allocated approximately ₹11,718 crore for this massive national exercise.
Important aspects for UPSC preparation include:
- Constitutional basis for census operations under the Seventh Schedule
- Historical evolution of census methodology in India since 1872
- Technological innovations in data collection and management
- Federal coordination challenges in implementing nationwide surveys
US Withdrawal from Climate Agreements: Global Implications
The United States has withdrawn from over sixty international organizations and agreements, including several climate-focused entities like the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. This follows the American exit from the Paris Agreement and reflects the Trump administration's skepticism toward multilateral climate initiatives.
Interestingly, the US has maintained membership in some environmental bodies including the UN Environment Programme and World Meteorological Organization, suggesting selective disengagement rather than complete abandonment of climate diplomacy. This approach allows continued influence over ongoing negotiations like the Global Plastics Treaty while distancing from commitments perceived as economically disadvantageous.
For UPSC candidates, this development raises questions about:
- The future of global climate governance without full American participation
- Comparative roles of institutions like IRENA and IEA in energy transition
- India's positioning in evolving climate diplomacy landscapes
- Implications for developing countries' climate financing and technology transfer
Healthcare Quality: The Lancet Commission's Findings
A recent Lancet Commission report highlights that poor healthcare quality contributes to approximately 1.6 million annual deaths in India—more than those resulting from lack of access to medical services. The analysis identifies deficiencies in provider training, irrational medication prescriptions, and inadequate adherence to clinical protocols as primary concerns.
While India has expanded healthcare coverage through initiatives like Ayushman Bharat, the commission emphasizes that quality improvement must become the central focus of health system reform. Recommendations include strengthening governance, enhancing community accountability, and leveraging technology for continuous performance monitoring.
UPSC relevance extends to:
- Constitutional provisions regarding public health and state responsibilities
- Performance evaluation of national health missions and insurance schemes
- Federal division of healthcare responsibilities between center and states
- Strategies for achieving Sustainable Development Goals related to health
These interconnected developments offer rich material for both preliminary and main examination preparation, requiring candidates to analyze policy implications, historical contexts, constitutional dimensions, and international ramifications across diverse subject areas.