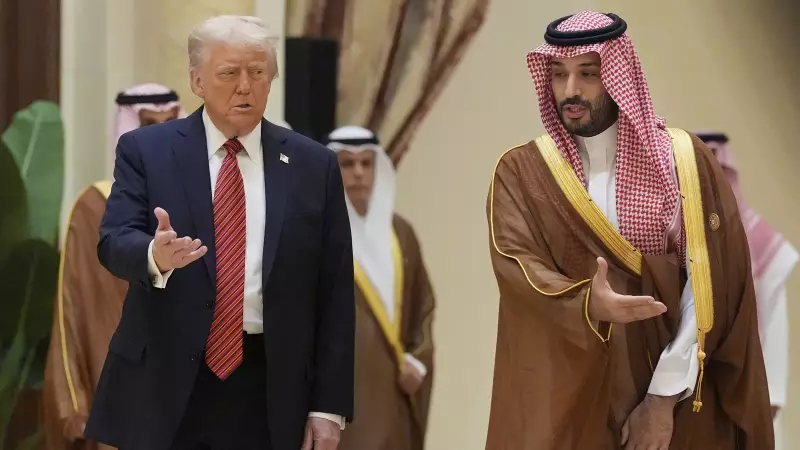
The high-profile visit of Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman to Washington this week represents a critical turning point in the decades-long relationship between the United States and Saudi Arabia, potentially setting the stage for a dramatic reshaping of Middle Eastern politics and economics.
The Historical Context and Modern Ambitions
This diplomatic engagement carries historical echoes of the landmark meeting eighty years ago between Prince Mohammed's grandfather, Abdulaziz ibn Saud, and US President Franklin Roosevelt aboard the USS Quincy in February 1945. That historic encounter established the foundation for a strategic partnership that would define America's Middle East policy and global energy security for generations.
The current meeting between MbS and President Trump aims to reboot this longstanding partnership through what observers describe as a comprehensive grand bargain. The agenda extends far beyond traditional oil discussions to encompass broad-based economic and technological cooperation, enhanced security arrangements, and fundamental reordering of regional alliances.
Saudi Arabia's Transformation Agenda
For Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, this visit serves multiple crucial objectives. Beyond strengthening bilateral ties, he seeks valuable American support for his impending succession. With King Salman now 89 and increasingly frail, the transition of power represents a delicate moment for the Saudi monarchy.
Equally important is securing robust US backing for Saudi Arabia's ambitious Vision 2030 agenda, which aims to transform the kingdom from a hydrocarbon-dependent economy into a diversified, globally competitive powerhouse. This unprecedented restructuring includes:
- Developing new industries in technology, tourism, and green energy
- Building massive projects like the NEOM future city
- Promoting social reforms and women's empowerment
- Advancing "moderate Islam" while reducing conservative clergy influence
In the security realm, Saudi Arabia seeks advanced weapons systems including the F-35 fighter jets, greater technology transfer, and pathways to developing domestic defense-industrial capabilities. Civil nuclear cooperation represents another priority, serving both energy diversification needs and symbolic parity with regional rival Iran.
The Palestinian Question and Regional Dynamics
The path to strengthened US-Saudi relations, however, faces significant obstacles. Riyadh has insisted on a "credible pathway" to Palestinian statehood as a precondition for normalizing relations with Israel. This creates a complex diplomatic challenge as Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu faces intense pressure from his far-right coalition partners to avoid any gestures toward Palestinian statehood.
President Trump is reportedly pressing Netanyahu to show flexibility, recognizing that Saudi-Israeli normalization could dramatically transform the Middle Eastern political landscape. The recent UN Security Council resolution on Gaza, passed with Russian and Chinese abstentions, provides some diplomatic momentum by endorsing a US-drafted plan for conflict resolution.
This resolution establishes an International Stabilisation Force composed largely of peacekeepers from Muslim nations and creates a "Board of Peace" to serve as Gaza's interim administration, with eventual authority transferable to a reformed Palestinian Authority.
MbS also wants Washington to acknowledge Saudi Arabia's emerging role as a rising regional and global actor. The kingdom has shed its traditionally passive foreign policy approach and is determined to establish itself as a consequential player in Middle Eastern and international affairs.
Strategic Implications and Future Prospects
For the United States, Saudi Arabia remains an indispensable partner in stabilizing the Middle East and maintaining American influence in the region. The potential expansion of the Abraham Accords through Saudi participation represents a key foreign policy objective for the Trump administration.
India, which maintains positive relations with both Israel and Saudi Arabia while strongly supporting the Abraham Accords, stands to benefit significantly from normalized ties between Tel Aviv and Riyadh. Such development could open new opportunities for Indian engagement in a more stable and prosperous Middle East.
However, the significant gap between Saudi demands for Palestinian statehood and Israel's current political constraints means expectations for an immediate breakthrough must be tempered. The success of this diplomatic reset will depend on creative solutions that address core concerns while allowing all parties to claim meaningful victories.
The outcome of these high-stakes negotiations could determine the future trajectory of Middle Eastern politics for decades to come, potentially creating a new regional architecture built on cooperation rather than conflict.