Climate Change's Complex Impact on Winter Storms: Arctic Warming and Jet Stream Weakening
Climate change is reshaping winter weather patterns in profound ways, with emerging evidence pointing to a weakening jet stream as the Arctic warms at an alarming rate. The Arctic is heating up nearly four times faster than the rest of the world, a phenomenon that has significant implications for global weather systems, including the intensity and frequency of winter storms.
The Science Behind Winter Storms and Climate Change
It is crucial to distinguish between weather and climate. While climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature and atmospheric conditions, weather describes short-term events. However, these two are intrinsically linked. Climate change alters the background conditions in the atmosphere, which can exacerbate extreme weather events. For instance, as the atmosphere warms due to the burning of fossil fuels, it retains more moisture. This increased moisture can lead to more intense precipitation, whether in the form of rain, sleet, or snow during winter storms.
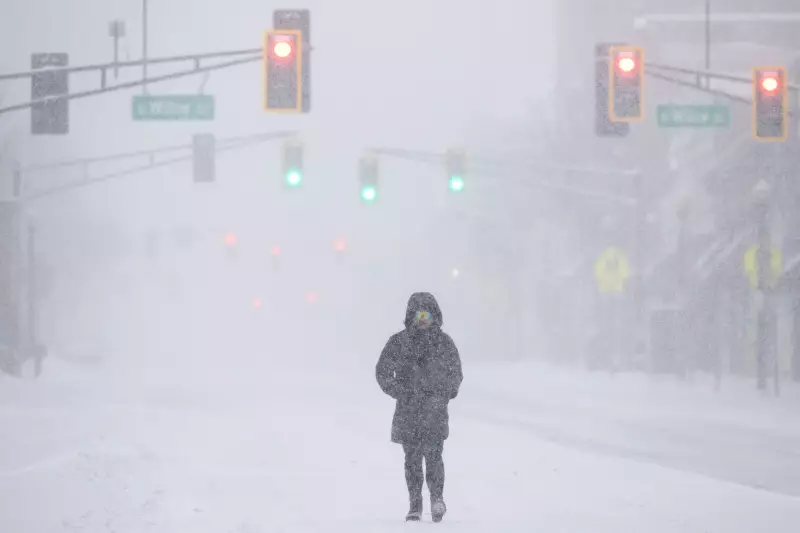
The recent frigid weather experienced in regions like Montclair, New Jersey, during a winter storm in January 2026, was driven by the polar jet stream. This fast-flowing air current high above the Earth typically confines cold air to the Arctic. However, there is growing evidence that the jet stream is weakening as the Arctic warms. This weakening can allow cold air to spill southward, leading to severe winter conditions in mid-latitude areas.
Debunking Climate Misinformation
Climate misinformation often surges around major weather events. For example, during cold snaps, some individuals, including former President Donald Trump, have incorrectly suggested that cold weather disproves global warming. This claim is scientifically unfounded. The world is unequivocally warming due to human activities, such as fossil fuel combustion, but this does not eliminate cold days. In fact, climate change can contribute to more extreme and unpredictable winter weather, including intense storms.
While the Arctic's role in global weather patterns is clear, scientists are still working to fully establish the connection between jet stream changes and Arctic warming. Ongoing research aims to clarify these complex interactions, but the overarching trend of warming and its impact on weather extremes is well-documented.
Renewable Energy and Weather Resilience
Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, are sometimes targeted during severe weather events, with claims that they are unreliable and contribute to power outages. However, evidence suggests otherwise. After the devastating winter storms in Texas in 2021, which caused widespread blackouts by knocking out over 70% of the state's electrical grid, some politicians blamed renewable energy. Peer-reviewed research has since revealed that the blackouts were primarily caused by freezing natural-gas pipelines and wellheads, not by wind or solar failures.
Moreover, studies indicate that renewable energy may enhance grid reliability during extreme weather. A 2024 analysis of hundreds of cities and thousands of blackouts found that areas with higher integration of renewables into their power grids were less vulnerable to outages. This highlights the potential for renewable energy to provide a more resilient and sustainable solution in the face of climate-induced weather challenges.
In summary, climate change is intricately linked to winter storms through mechanisms like Arctic warming and jet stream weakening. Debunking misinformation and understanding the science behind these phenomena is essential for informed public discourse and effective policy-making. As the world continues to warm, embracing renewable energy and robust climate strategies will be key to mitigating the impacts of extreme winter weather.