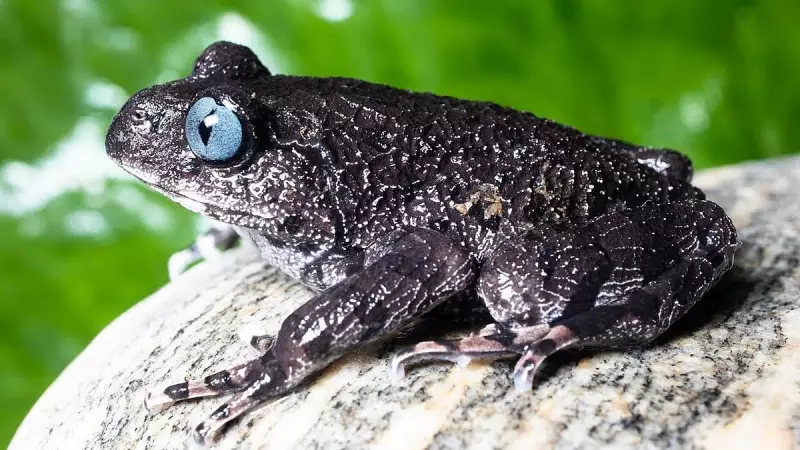
In a significant boost to India's biodiversity records, scientists have identified two previously unknown species of frogs in the remote landscapes of Arunachal Pradesh. This exciting discovery underscores the rich and still largely unexplored ecological wealth of the northeastern state.
The Discovery in Detail
The finding was officially reported on 09 January 2026. The newly discovered amphibians belong to the Megophryidae family, which is recognized globally as one of the most diverse frog families. This family, which includes the distinctive Asian horned frogs, now boasts 366 recognized species worldwide, with these two additions from India.
One of the newly identified species has been named the Mechuka Slender Arm Frog, a name derived from its location and physical characteristics. The discovery was a result of meticulous fieldwork and taxonomic analysis by dedicated Indian researchers, highlighting the importance of sustained scientific exploration in biodiversity hotspots.
Significance for Biodiversity and Science
This discovery is not just about adding new names to a list. It has profound implications for understanding evolutionary biology and ecosystem health in the Eastern Himalayas. Arunachal Pradesh, part of the Himalayan biodiversity hotspot, is a treasure trove of endemic species, and each new find helps piece together the complex puzzle of the region's ecology.
The identification of the Mechuka Slender Arm Frog and its counterpart expands our knowledge of the Megophryidae family's distribution and adaptation. It also emphasizes the critical need for conservation efforts in these fragile habitats, which are often threatened by climate change and human activity.
Looking Ahead: Conservation and Research
The revelation of these two new frog species serves as a powerful reminder of the hidden biological wonders within India's borders. It reinforces the necessity for continued and enhanced scientific surveys in remote areas. Protecting these species and their habitats is paramount, as they may hold keys to scientific knowledge and ecological balance.
This achievement by Indian scientists puts a spotlight on the country's role in global biodiversity documentation and conservation. It encourages further investment in taxonomic research and the protection of pristine environments like those found in Arunachal Pradesh.